Summary
- Function의 기본적인 동작 원리: receive input data, transform data, and then output data
- Parameters: placeholders to receive input values. Like local variables of a function
- Function body: block of code that we want to reuse. Processes the function's input data
- return statement to output a value from the function and terminate execution
- Calling, running or invoking the function, using () bracket
- Arguments: actual values of function parameters, to input data
const calcAge = function (birthYear) {
return 2037 - birthYear;
}
const yearsUntilRetirement = function (birthYear, firstName) {
const age = calcAge(birthYear);
const retirement = 65 - age;
if (retirement > 0) {
return retirement;
console.log(`${firstName} retires in ${retirement} years`);
} else {
return -1;
console.log(`${firstName} has already retired 👏`);
}
}
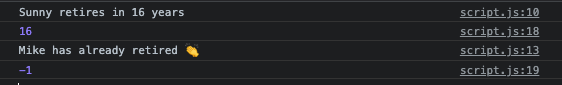
console.log(yearsUntilRetirement(1988, 'Sunny'));
console.log(yearsUntilRetirement(1950, 'Mike'));이렇게 return 다음에 console.log문을 적어주면? 실행 안됨 🙅♀️
왜냐면 return 하고 바로 해당 코드 블록을 빠져나오기 때문!
so return과 console.log의 위치를 바꿔주면 된다.
(커서를 console.log에 두고) 단축키로 how? option + 방향 키 🔼
그럼 이렇게 코드 줄이 위로 이동한 걸 볼 수 있음!
if (retirement > 0) {
console.log(`${firstName} retires in ${retirement} years`);
return retirement;
} else {
console.log(`${firstName} has already retired 👏`);
return -1;
}
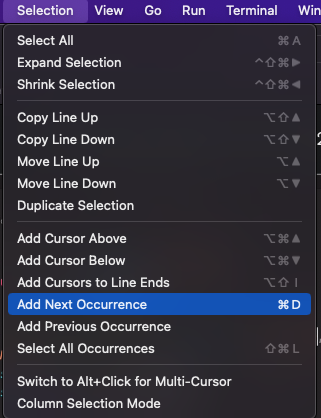
다른 유용한 단축키 cmd + D
같은 value 한번에 수정할 수 있음
'Programming > JavaScript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Introduction to Arrays (0) | 2022.09.10 |
|---|---|
| Coding Challenge #1 - who's win? (0) | 2022.09.09 |
| Functions Calling Other Functions (0) | 2022.09.03 |
| Arrow Functions (0) | 2022.09.03 |
| Function Declarations vs. Expressions (0) | 2022.09.03 |
